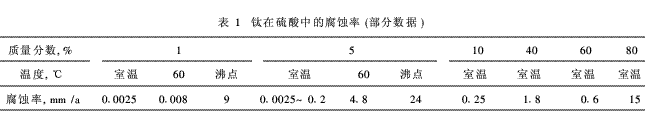
Abstract : This paper introduces the purpose of electroplating solution filtration, selection, installation, use and maintenance of filter; heating method and heat source, heater material, surface power, automatic control of temperature controller and temperature probe selection; cooling method and The application of cooling titanium tubes in anodizing. Key words : electroplating equipment; solution filtration; heating; cooling 1. Filtration of plating solution 1·1 Purpose of filtering 1·1·1 extended service life Filtration of the solution primarily acts as a purification solution. When the impurities such as oil stains in the degreasing liquid are heavy, the degreasing effect is deteriorated, the supplementary material is increased, and the liquid temperature used is increased. If not filtered, the degreaser can usually only be partially or completely renewed. To this end, Mr. Xiang Rong Lao specially developed a degreasing filter, which not only improves the degreasing effect, but also greatly prolongs the service life of the degreasing liquid. Electroless plating is an autocatalytic reduction process. When there are fine solid particles in the plating solution, it becomes a catalytic reduction center, and the main salt metal ions in the plating solution which are not high in content are not consumed on the workpiece but are quickly reduced on the particles, and the plating solution is consumed. Will expire quickly and be scrapped. Only by timely removing these particles by filtration can the life of the electroless plating solution be ensured or extended. 1·1·2 Reduce plating solution failure and improve coating quality Even if the solid particles in suspension in the plating solution reach the surface of the cathode and adhere to the surface of the coating by diffusion, convection, electrophoresis, etc., there are many failures, resulting in rework or even scrapping of the workpiece. For bright plating, it will reduce the brightness and flatness of the coating, and the product will not be qualified. For example, the dye aggregate in the high dye type bright acid copper liquid produces grit in the plating layer, and the Cu2O copper powder in the copper acid solution generates Cu2O copper powder to lose the light, slow the light, and adjust the level; Fe in the nickel plating solution ( OH)3 causes pinholes and pittings in the coating; when the porosity of the coating is high, the corrosion resistance is greatly reduced, and sometimes the plating layer has to be thickened, resulting in a decrease in production efficiency and an increase in cost; and various large mechanical particles cause burrs of plating. Rough and must be reworked. Any mechanical impurities that are suspended or coarse can only be removed by careful filtration of the bath. Only by keeping the bath highly clean can it reduce failures, reduce rework, improve quality, reduce overall costs, and increase market competitiveness. 1·1·3 Removal of plating bath impurities It is inevitable that the plating solution will generate and accumulate various harmful impurities. When it exceeds the allowable value, it causes various failures. There are several ways to remove impurities: (1) Various mechanical impurities are directly removed by filtration. (2) Mechanical impurities formed by conversion, removed after filtration. For example, excessive Cl- and Cu+ in the copper acid solution form CuCl precipitation, Fe3+ in the nickel or chloride galvanizing solution forms Fe(OH)3 precipitate, and Fe2+ in the HEDP copper plating solution forms Fe(OH)2 precipitate. . Direct filtration removes these impurities. CO2-3 is inevitably produced in the alkaline plating solution, which is harmful when excessive. In the cyanide copper plating and zincate galvanizing solution, too much C02-3 is saturated and crystallized into solid Na2CO3·nH2O when the liquid temperature is low, and can be removed after filtration. (3) The soluble impurities are removed by filtration in a solid form. This is a very common method of handling impurities. For example, in the galvanization of potassium chloride, Fe2+ is converted into Fe3+ by oxidation, thereby forming a flocculent Fe(OH)3 precipitate, and Cu2+ and Pb2+ impurities in the liquid are added to the zinc powder to replace the precipitate, cyanide copper plating, HEDP copper plating, and nickel plating liquid. The very harmful Cr02-4 is reduced to Cr3+ by adding insurance powder (sodium dithionite) to form Cr(OH)3 precipitate; Cu2+ in the nickel plating solution is added to the yellow blood salt to form a precipitate, and Cu2+ is added to the sodium sulfide in the acidic bright tin solution. A precipitate is formed, and β-stannic acid is added to the flocculant to flocculate and precipitate; the organic impurities adsorbed by the activated carbon in the plating solution are added to the activated carbon for adsorption and precipitation. 1·2 filtered form 1·2·1 fluted filter The tumbling filter refers to filtering the solution from the original working tank to other clean tanks by pump or manual boring, cleaning the working tank (cleaning the anode bag and anode at the same time for electroplating), and then filtering (or directly) returning The original working tank is supplemented with the working fluid. The tumbling filter has a good filtering effect and the filtering is thorough. The following conditions must be filtered: (1) When a large amount of solid precipitate is generated by treatment of impurities in the plating solution; (2) Continuously filtering more precipitates that are difficult to remove and accumulate at the bottom of the tank or at the corners; (3) Chloride galvanizing, iron removal, etc., acid bright tin plating in addition to tetravalent tin compounds, Cu2+ impurities, etc., after siphoning the upper supernatant, manually re-filtering the mud feet to reduce the loss of plating solution; (4) When there is a large amount of surface area in the working tank such as the plating tank, it needs to be removed. 1·2·2 continuous loop filtering Continuous loop filtration is less efficient than tumbling filtration, but does not cause a shutdown. Continuous circulation filtration is to extract the solution from the bottom of one end of the working tank and filter it back to the other end of the tank. The purpose is to keep the working fluid clean. Since the filtered solution is mixed with some dirty solution, the solid impurities can be gradually reduced, and the efficiency is lower than that of the tumble filtration. The purpose of the circulation filtration is mainly to keep it clean, so the premise is that the solution itself is relatively clean, so the circulation filtration should be carried out on the basis of the tumble filtration. If the solution itself is very dirty and there are more mud feet at the bottom of the tank, it will be recycled and filtered, but the mud feet will be turned up, and the working fluid will be dirty or even impossible to produce. If the actual flow rate of the filter is too small and the removal rate of solid impurities is less than the generation speed, the circulation filtration will lose its meaning. When the plating solution is air-mixed, if there is a mud foot at the bottom of the tank, it will inevitably be stirred up, and continuous circulation filtration must be used. It is most advanced when the plating solution is subjected to cyclic filtration while continuously electrolyzing to remove metal impurities in the plating solution which are easily removed by small current electrolysis. At this time, the plating solution overflowing from the plating overflow port is first collected in a small tank, and the plating liquid is extracted from the small tank and filtered into the filter, and then returned to the other end of the plating tank. A small rectifier and a plate are additionally arranged on the small groove, and the impurities are continuously treated by small JK. When the brightener is continuously added, it can be added to the small tank and naturally mixed evenly through the filter. When the zincate is galvanized, all the insoluble iron anodes are placed in the plating tank, and 0# zinc is added as a zinc dissolution tank in the small tank to supplement the zinc, which is better than the mixed iron plate and the zinc plate in the plating tank. In the copper-nickel-chromium process, the copper impurities which are easily introduced by the continuous electrolysis of the bright nickel liquid are much better than the chemical precipitation treatment or the addition of the water removal when the copper impurities are excessive. 1·3 filter selection 1·3·1 filter flow The nominal flow rate (t/h) of the filter is the maximum flow of filtered material through the clean water without any blockage. Because the actual flow rate of the filter is a variable and cannot be marked; as the filter residue on the filter material accumulates, the resistance becomes larger and larger, and the pressure inside the machine becomes higher and higher (the modern filter is equipped with a pressure gauge), and the actual flow rate It is getting smaller and smaller. Therefore the actual flow is always lower than the nominal flow. For cyclic filtration, the nominal flow rate should be 8-12 times the volume of the bath. 1·3·2 Filtration accuracy The filtration accuracy means that the filter material of the filter can filter out the minimum particle size (μm) of the solid particles. The actual accuracy is also a variable: when the filter residue (or filter cloth, filter paper, etc.) accumulates more slag, the more small pores in the upper part are blocked, the filtration accuracy will gradually decrease. There are several factors that affect the actual filtering accuracy: (1) The influence of the filter material. The same filter, using different precision filter materials, the filtration accuracy is not the same. For example, the polypropylene thread wound honeycomb filter has a nominal accuracy of from 0. 2μm to 20μm. Switching to a different filter can change the filtration accuracy. (2) The structural influence of the filter. For a time, laminated platen filters were very popular, but after use, the filtration accuracy was very poor, and the nominal accuracy was not achieved. Zhejiang Tonglu Sanda Filter Factory has carried out many researches on this issue. At first, I suspected that the filter cloth was not accurate enough. It was not acceptable to use the imported high-quality filter cloth. Later, it was found to be a pressure plate problem; the national product is a PP material pressure plate for the injection molding of the imported product size, but the mechanical strength of the pressure plate of the domestic PP material injection is not enough, and the thin portion is formed around the middle after the compression, and the solution part is straight-through. Finally, the mold has to be modified, and the pressure plate is thickened to improve the mechanical strength, and the precision is improved. In the case of a wire-wound filter element, a filter element is pressed against the filter element at the same time by a filter cartridge. However, due to the error of the filter element length and the deformation during use, a part of the filter element is tightly sealed and sealed. If it is a little short, the pressure is not tight and there is a weak point. If the pressure is not pressed, the resistance is small, and the filtrate is also straight. Now it has been changed to a single filter with a cock. (3) The impact of installation and bad. If there are large particles of mechanical impurities, the pressure is not tight. If the rubber gasket is lost when the filter element is installed or there is a large amount of mechanical impurities on it, the pressure is not tight, and the weak resistance is also caused. Therefore, you should operate it carefully when installing the filter element. The choice of filtration accuracy depends on the solution requirements. There is a contradiction between them: the higher the filtration precision, the cleaner the filtration, but the faster the filter material is blocked, the faster the actual flow rate drops, the more frequent the filter cleaning, the more difficult the cleaning is completely. Electroless plating solution requires high precision, should be above 2μm, copper plating and nickel plating 5μm is good, galvanizing liquid is dirty, 10μm-20μm, the requirements are not too high, and the cleaning is too frequent when the precision is high. 1·3·3 Filter pump selection (1) Magnetic pump In the past, PTFE was used for the shaft seal material of centrifugal pumps, and the wear resistance was insufficient. The leaking liquid at the shaft seal causes the solution to be lost. Therefore, the magnetic pump without shaft seal is used instead of leaking. However, after use, I found several problems: 1 The introduction of ferromagnetic material causes the pump to wear very quickly. The gap between the rotor and the stator in the magnetic pump is inherently small. If the ferromagnetic powder slag is introduced, it will be firmly absorbed by the permanent magnet in the pump to form an abrasive. The injection layer outside the permanent magnet is worn through and the magnet is rotted. In the plating solution, it is inevitable that the workpiece is corroded, and the nickel slag and the like form ferromagnetic powder and chips, so the magnetic pump has a short service life. 2 The magnetism of the magnet in the magnetic pump will gradually decline (especially when the quality of the magnet is bad), causing the transmission torque to decrease, the pump head and suction range to decrease, and the pressure inside the filter to decrease. Therefore, the magnetic pump is rarely used on the filter. It is expensive for plating such as silver plating and gold plating, but the plating volume is generally not large. It is not easy to introduce ferromagnetic impurities. It is still advisable to use the nominal power. Large imported small filter for magnetic pumps. Although expensive, the proportion of total investment is still small. (2) Improved centrifugal pump The filter is now mostly modified centrifugal pump. The shaft sealing material is changed to a silicon carbide material with high hardness, high wear resistance and high flatness, which is much better than the original polytetrafluoroethylene material. After several years of normal use, the shaft seal is still leaking. (3) Self-priming pump The self-priming pump has a strong suction force, and has a vacuum suction capability in the inlet pipe, but the utility model has high cost, and when the internal wear gap is large, the self-suction capability is lost, so it is rarely used. (4) Submerged pump The impeller of the submerged pump is directly immersed in the solution and can be used after being turned on. However, when the pump shaft is too long, it is easily deformed and damaged. When the pump is integrated with the filter, it becomes a submerged pump filter. However, it is mostly miniaturized, otherwise the area occupied on the trough is too large. After the shaft is short, it can only be pumped from the middle, and the bottom dirty liquid is not easy to extract. Small volume tanks are available for air agitation. 1·4 Installation and use of filters 1·4·1 installation height When the filter is installed, the upper edge of the filter cartridge must be higher than the liquid level of the reservoir. Otherwise, after cleaning the filter cartridge to open the filter cartridge cover, the solution will overflow from the upper part of the cylinder due to the difference in liquid level. Such problems have arisen in large production. 1·4·2 test machine The filter is strictly prohibited from idling, otherwise the pump will wear out quickly. After the installation of the inlet and outlet pipes is strict, the water should be added according to the instructions of the instructions. For the filter with three-phase motor, when it is determined that there is no phase loss in the power supply line, after the water is poured, first start the motor for several tens of seconds and then shut down, and carefully check whether the direction of the arrow between the motor steering and the on-board mark matches, if it does not match. , the two live wires should be exchanged arbitrarily to make the motor turn and change. If the steering is not correct, the flow rate of the filter will be small, and the pressure on the machine will not rise or rise very little. 1·4·3 Maintenance (1) Filter cleaning The gauge pressure display should be observed in time. If the gauge pressure has not risen, it means that the filter element is not installed, and there is a weak leak, it should be disassembled and reinstalled. When the gauge pressure is close to the red line mark, it indicates that the filter element has been blocked seriously. The actual flow rate is very small. The filter element should be taken apart and cleaned. If the pointer has reached the red line mark range, it must be cleaned. Care should be taken carefully, carefully and repeatedly when cleaning the filter element. For potassium chloride galvanizing solution and nickel plating solution, the filter element is sometimes difficult to clean, and the yellow plug is excessive (mostly iron hydroxide precipitation), which can be further washed after being soaked in dilute hydrochloric acid for a period of time. However, for acid copper, bright acid tin, chrome plating, etc., it is strictly forbidden to soak with hydrochloric acid, otherwise it will not be washed. (In the large production, workers have been immersed in the bright acid copper filter filter cleaning with hydrochloric acid. The liquid introduces too much C1 - a serious accident that is difficult to handle and scraps the plating solution). The upper edge of the filter cartridge should be cleaned and there should be no foreign matter on the O-ring. All bolts should be tightly tightened, too loose and too tight. If it is too tight, the slippery wire will be damaged. (2) Cleaning and anti-corrosion Good habits of caring equipment should be developed. In some places, the dust on the filter is very thick, and the salt crystals are not cleaned. It is best to apply a thin layer of butter to the exposed parts such as the shaft. In many places, the corrosion is very serious and it is not treated. When flushing with water, water cannot enter the motor and power switch box. It is best to scrub in time instead of rinsing with water. 1·5 Other issues 1·5·1 pipe fixing Most pipe clamps are galvanized with iron parts, one is very easy to spin the wire, and the other is poor corrosion resistance (stainless steel is not resistant to corrosion in the electroplating workshop). Therefore, it is better to use a thick wire to tighten the pipe joint. The inlet and outlet fluid wire tubes inserted into the plating solution should be managed to be firmly clamped on the grooves without falling out of the grooves. In the case of excessive production, many accidents have occurred, and many plating solutions have been lost due to siphoning. 1·5·2 Discharge in the machine The bright nickel liquid has high boric acid content and is easily crystallized after liquid cooling. In the single-shift production, it is best to discharge the liquid in the filter after the machine is shut down, so as to prevent the boric acid from crystallization in the machine to block the filter and crystallize in the pump, so that the motor will be burned when the machine is turned on the next day. Large accidents have occurred in the case of bright nickel-iron alloy plating. The best method is to weld the filter inlet valve and the reducer tee to the side of the bottom of the plastic tank. A drain valve is arranged on the tee. After the shutdown, the main valve and the liquid discharge valve are closed. The plating solution in the machine flows into the plastic basin through the drain valve and returns to the plating tank. Before the second day of work, the liquid discharge valve is closed, and then the liquid total valve is opened. The filter can be self-irrigated and then started for circulation filtration. 1·5·3 bottom valve selection The general filter is equipped with a liquid inlet valve valve assembly, which serves two functions: one is to avoid the damage of the pump caused by the large debris entering the filter pump, and the other is to close the bottom valve during the water diversion, and it is easy to inject water into the inlet pipe. Exclude air. Many people suspect that they are inconvenienced or abandoned. It is best to use it, especially when the inlet pipe is long. 1·6 plating solution difficult to mechanically filter 1·6·1 Fluoride-containing plating solution For a fluorine-containing heavy chrome plating solution (not suitable for a fluorine-containing heavy chrome plating additive) or a fluoroborate plating solution, it is difficult to continuously filter with a filter. The reason is that although most of the parts are plastic, it is difficult to find fluoride-resistant materials. Magnetic pumps are useful for ceramic shafts but are also resistant to fluoride corrosion. Stainless steel and even titanium are not resistant to fluoride corrosion. The mechanical strength of the all plastic shaft is not enough. This type of pump can be used for a long time only after solving the problem of metal shaft resistance to fluoride corrosion. 1·6·2 Electroless plating solution When working in a plastic electroplating factory, the chemical copper sinking process began. In order to save costs, copper sulfate, sodium potassium tartrate and the like are all industrial grade materials, the electroless copper plating solution is dirty, and the autocatalytic reduction is fast. I have tried to use a filter to filter the room temperature electroless copper plating solution continuously, but after two days, a thick layer of copper is reduced in the plastic tube and the pump, and I dare not use it again. The slightly acidic electroless nickel plating solution has high requirements on the cleanliness of the plating solution, otherwise it will quickly become an autocatalytic reduction center on the fine precipitate and the plating solution will be quickly scrapped. It is reasonable to use a precision 2μm filter for cyclic filtration. The liquid temperature is as high as 90 °C, and the high temperature resistance of the filter can be solved. However, the precipitated residue on the filter element becomes a catalytic reduction center, and a nickel layer is deposited on the filter element, which is difficult to solve. Nowadays, the so-called special filter for electroless nickel plating is nothing more than a filter material that is resistant to concentrated nitric acid. After frequently taking out the filter element, after washing with water, the chemical nickel layer deposited on the filter element is removed with concentrated nitric acid, and then carefully cleaned. Direct filtration at working fluid temperature, in theory, can not fundamentally solve the nickel deposit of the filter element. The author believes that high-temperature electroless nickel plating can only use intermittent filtration: when the liquid temperature is reduced to a non-reactive temperature below 70 °C, the plating solution is carefully filtered. If the production volume is large, there should be two tank plating fluids for rotation. In this way, the heating energy consumption will be larger. If there is only one tank plating solution, it can only work intermittently: after the liquid is considered dirty, stop working, use a titanium serpentine tube to cool the water to 70 °C or less (with a digital display thermostat), and quickly turn the tank to filter. Another plating tank of the facility (the large-capacity filter can also be continuously filtered for a period of time), and then quickly heated to the working fluid temperature to continue production. 2. Heating of the plating solution 2·1 steam heating The advantage of steam heating is that the heating rate is faster, especially when the working bath volume is large. The working fluid is heated, and a corrugated tube is made of a corrosion-resistant and heat-conductive metal tube, placed on the bottom of the tank or on the side of the tank, and steam is introduced from one end, and the gas is used to heat the hot water tank. There is also a tube-type heating, the heating tube is placed at the bottom of the tank, and the heating is relatively uniform, but it is not conducive to salvage the parts, so the heating method on the groove side is more. The hot water tank can be directly flushed into steam to heat, and the heat efficiency is high, but if no noise elimination device is provided, the noise is large. For working fluids such as plating solution, it is not possible to use steam to straighten. Otherwise, the introduction of impurities is high. Second, the condensed water causes the solution to be diluted and the volume is continuously increased. Dry the workpiece and also use a steam oven heated by a steam tube. When a high-pressure boiler is used and the high-pressure steam generated is sent to the electroplating workshop, the pressure-reducing valve should be used to reduce the steam pressure to 0. 2 MPa for steam supply, otherwise the valve, elbow, tee, etc. are easily damaged. The alkaline high-temperature blue-blue liquid of steel parts should not be heated by steam. Otherwise, if the heating pipe buried in the liquid leaks, it will cause the blue solution to boil and splash out. Easy to cause injury. Steam heating has the following disadvantages: (1) A steam boiler is required to provide superheated steam. There are many problems in burning boilers, such as: 1 need to soften the boiler water; 2 need to operate with a special boiler for operation of the license; 3 boiler pressure vessels, need to stop the furnace cleaning scale every year, by the law enforcement department Regular annual inspection, after the annual inspection is qualified, can continue to use: 4 boilers with more coal (there are also natural gas burning places), the treatment requirements for soot are getting higher and higher, and the compliance is difficult; 5 regardless of natural gas and coal, the price rises. Soon, the cost is getting higher and higher. Boilers have been restricted or banned in many cities and suburbs. (2) It is difficult to achieve automatic temperature control. On the one hand, automatic temperature control requires the use of high-quality, durable steam solenoid valves to control steam supply and stop supply; on the other hand, to provide steam supply without interruption, batch furnaces can not achieve automatic temperature control. Therefore, steam heating is rarely used unless there is concentrated heating in a large electroplating plant or industrial park in a remote location. 2·2 circulating hot water heating For solutions that do not require a high heating temperature, hot water can be circulated through a serpentine heating tube for heating. Some self-employed households burn small-scale boiling water boilers. When the water in the furnace is burned to 80 °C-90 °C, the hot water is sent to the heating pipe by the pipeline pump, and the water is returned to the small boiler. For a period of time, the "energy-saving treasure" of burning diesel oil was applied, and it was also heated by hot water for circulation; when the price of diesel oil rose sharply, the "energy-saving treasure" was eliminated. When heated with circulating hot water, the heating rate is slower. The heating of hot water for high-temperature scalding is still supplemented by electric heating. 2·3 direct heating of coal stove In order to save, some township and village enterprises directly burn coal or natural gas to the bottom of the tank for chemical cooking oil tanks and alkaline high-temperature blue tanks. There is not much trouble in burning the boiler, and it also saves money. However, there is also a problem of dust control in burning coal. It should be noted that the mud at the bottom of the tank should be cleaned up in time. There was once a factory where the mud at the bottom of the chemical degreasing tank was too thick, the heat transfer was bad, and it suddenly burst, causing the chemical degreasing liquid to splash out, and the operators were severely burned. The treatment cost cost tens of thousands of yuan. 2·4 electric heating Due to the problems and limitations of steam heating, most electroplating plants have switched to electric heating. Electric heating is a clean energy source for electroplating plants and does not cause environmental pollution. Another advantage of electric heating is the ease of automatic constant temperature control of the solution. The disadvantage of electric heating is that the heating rate is slower and the electric power requirement is larger. For example, the solution of the solution tank without the insulation layer is: 1000L solution, heated from 30 ° C to 55 ° C, if it takes 1 h to heat up, the electric power should reach 69 kW. Be sure to pay attention when using electric heating: (1) When using single-shift production, it is necessary to use constant temperature control facilities, and keep warm at constant temperature when not in production. If the bath is stopped and cooled to room temperature, it will be heated in advance at night. When the temperature is constant to the working temperature, it will work when you go to work. Otherwise, it will be heated when you go to work, and it will take a long time to produce. (2) Where the working tank for heating is provided with insulation layer. Although the investment is large at one time, the long-term energy-saving effect is obvious. The additional investment added with the insulation layer can be recovered quickly, otherwise it will not be worth the candle. It also does not meet the policy requirements of “energy saving and emission reductionâ€. When not in production or when preheating, the notch should be covered with a thick plastic sheet to cover the surface. Some people are willing to use their brains to cover a plastic quilt on a plastic cloth at night. The effect of preventing heat loss is obvious and worth learning. 2·5 jacket groove indirect heating For solutions that are susceptible to corrosion (such as fluoroborate tin-lead alloy) and some that do not allow local overheating when heated, require a homogeneous solution (such as a slightly acidic electroless nickel plating solution) and both heat and cooling. Solutions (such as aluminum electro-polishing, size chrome), and sometimes jacketed tank heating. There are several issues to be aware of in the jacketed tank heating: (1) Thermal conductivity and corrosion protection of the inner groove When the jacket groove is heated, an outer groove with sufficient mechanical strength is disposed at a certain distance outside the inner groove, water is introduced into the jacket, and steam or electric heating is applied to the water in the jacket, and heat is transferred to the solution through the inner groove. It has a large heating area, uniform heating, and no local overheating. The choice of the material of the inner tank is both anti-corrosion and good thermal conductivity. 1 hard chrome plating can be used in industrial pure titanium metal, the effect is good, but the cost is high. Units with strong financial strength are sometimes used. 2 Electroless nickel plating can be used in carefully passivated stainless steel tanks (sometimes with anodized protection) or acid-resistant enamel tanks. 3 Electro-polishing uses a thin stainless steel or carbon steel tank lined with lead plates (titanium grooves are not resistant to corrosion). The 4 fluoroborate plating tank is generally small, and a thin polyvinyl chloride tank is used. (2) Water level problem in the jacket Due to the heat conduction problem of the inner groove, the inner groove is thin and the mechanical strength is insufficient. However, when the water level in the jacket is sufficiently high, the solution and the jacket water are substantially in a state of pressure equilibrium, and the inner groove is under a small force. To this end, it should be ensured that the water level in the jacket is high enough. In order to timely replenish the evaporation loss of the water in the jacket layer, it is preferable to set the water level automatic control facility. In order to easily observe the water level, at least a water level gauge should be set up like a boiler to replenish water in time. The jacket tank is provided with an overflow water outlet, and the control liquid level is not too high. (3) Temperature control A digital display temperature controller is used, and the temperature control probe is placed in the working fluid. When the jacket water is electrically heated, the power supply of the electric heater is controlled to be turned on and off. When heated with steam, the steam supply is controlled by a steam solenoid valve. For the electropolishing and hard chrome plating processes with high current density and fast plating temperature rise during production, the temperature should be heated to the working fluid temperature at the beginning, and then cooled by cold water. When the working fluid temperature is reached, the heating source should be cut off. The temperature controller is only used to monitor the liquid temperature. When the steam is heated, the manual steam valve is closed and the cold water is turned off; when the electric heating is turned off, the heating power is turned off, and the cooling water supply valve is turned on to supply the cooling water. According to the temperature controller, the liquid temperature value is adjusted to adjust the cold water supply amount, so that the liquid temperature is maintained within the allowable range of the process. The cooled effluent is used as washing water. 3. Heating and cooler materials 3·1 Titanium 3·1·1 Titanium corrosion resistance principle Titanium itself is a very active metal that can even displace hydrogen from water. Titanium is widely used as an anti-corrosion material because it is extremely easy to passivate. The surface is easily formed by a dense oxide layer and passivated. Among all metals, the passivation coefficient of titanium is the largest, reaching 2.44. This passivation film protects the titanium itself from corrosion under a variety of media conditions. (1) Titanium is naturally passivated very quickly in the atmosphere. (2) Titanium is passivated under the action of dissolved oxygen in water. (3) In an electrolyte solution containing a metal ion having an oxidizing high valence state, the oxidation property of a high-valent ion keeps the titanium in a passive state. For example, the aluminum ion in the aluminum anodizing solution has only a trivalent state without bivalent and monovalent, and the sulfuric acid content is high, so it is not resistant to corrosion. However, in the bright acid copper plating solution of sulfate, although the sulfuric acid content is also high, the copper ion is in a high valence state of Cu2+, and the titanium is passivated, and the titanium is resistant to corrosion. (4) Corrosion resistance under any oxidizing medium conditions. For example, Wangshui is a mixture of two acids, "three salts and one nitrate", which dissolves gold, but the oxidation of nitric acid is sufficient to keep the titanium in a passive state. Aromatic water cannot dissolve titanium at room temperature. (5) In the dry chlorine gas, titanium is corroded to form TiCl4 at room temperature, but in a chlorine gas containing a certain amount of water, titanium is in a passive state. (6) In a weakly acidic, neutral and alkaline solution, it is inactivated by interaction with dissolved oxygen in the liquid and anion such as OH- in the electrolyte. (7) In addition to formic acid, oxalic acid and relatively concentrated citric acid, titanium has excellent corrosion resistance to all organic acids. In a corrosive medium, the application of anodic protection can improve the corrosion resistance. 3·1·2 Not suitable for titanium use Where the passivation film of titanium is destroyed, titanium is not resistant to corrosion and cannot be used as a heating and cooling material. (1) Any fluoride is easily destroyed by the passivation film of titanium. Hydrofluoric acid and fluorosilicic acid are the most corrosive to titanium. Very dilute hydrofluoric acid also quickly erodes titanium: 2Ti+6HF=2TiF3+3H2↑ Titanium is severely corroded in fluoride-containing acidic media, including fluorosilicic acid, fluoroboric acid. Therefore, titanium is not suitable for any fluorine-containing boric acid, fluorosilicate plating solution, fluoride-containing composite catalytic chrome plating solution (including the use of a slightly more fluorine-containing chrome plating additive), bright nickel nickel plating solution with fluoride additive, etc. Fluorine-containing solution. (2) Titanium is not resistant to pure reducing medium corrosion. When titanium is used in pure hydrochloric acid, it has a mass fraction of 7.5% or less at room temperature, 3% or less at 60 ° C, and 0.5% or less at 100 ° C. However, hydrochloric acid contains chlorine gas, nitric acid, sodium hypochlorite, chromate, Fe3+, Cu2+, and a small amount of precious metal, and titanium can be passivated and used. In sulfuric acid solution, the corrosion resistance of titanium decreases with the increase of sulfuric acid concentration and liquid temperature: 20% sulfuric acid can be resisted at 0 °C, sulfuric acid can be only 5% at room temperature and oxygen, only 100 °C Can remain passive in 0. 2% sulfuric acid. The main substances that inhibit corrosion of titanium in sulfuric acid solution are: Fe3+, Cr02-4, MnO2, HNO3 and chlorine. The addition of hydrogen peroxide to sulfuric acid not only is not conducive to the passivation of titanium, but accelerates the corrosion of titanium, because H202 will dissolve and dissolve titanium. Titanium has poor corrosion resistance in pure phosphoric acid. At 35 ° C, only the phosphoric acid with a mass fraction of 30% or less is resistant. At 60 ° C, the annual corrosion rate of titanium in 10% phosphoric acid is about 0.13 mm, and at 100 ° C, it can only resist 3% or less of phosphoric acid. Fe3+, Ag+, Hg2+, and HNO3 have certain corrosion inhibition properties. Therefore, in a phosphoric acid-sulfuric acid chemical or electrochemical polishing liquid, neither a titanium heater nor a titanium tank can be used. (3) Titanium generally has corrosion resistance in an alkaline solution. It is better than the corrosion resistance in KOH liquid in NaOH solution. However, in a mixture of a base and hydrogen peroxide, titanium is not resistant to corrosion. H202+OH-=H0-2+H20 H0-2+Ti+30H-=Ti(OH)202+H2O+4e (4) Titanium workpieces are often pickled with hydrofluoric acid hydrofluoric acid before plating (titanium baskets, etc., after appearance, beautify the appearance, sometimes pickling to remove argon arc welding and improve brightness). It should be noted that pickling is an exothermic reaction that causes the liquid temperature to rise; HNO3 decomposes faster. In red smoke nitric acid, when the excess NO2 exceeds 2% and the water content is insufficient, the reaction may cause an explosion due to the exothermic heat. Under the action of red smoke and nitric acid, a slight impact or friction will produce a spark, causing a violent explosion. The author was originally in a state-owned enterprise. Because of the excessive loading of the short-cut titanium tube during pickling, a vicious explosion occurred. To draw attention to this. 3·1·3 corrosion of titanium welds When titanium is welded (usually using argon arc welding), if it cools quickly, microscopic internal stress is generated. At the same time, due to the diffusion and accumulation of hydrogen, the compressive stress causes microscopic cracks, and the crack increases when used. Due to the action of hydrogen or oxygen, small pores are formed near the fusion point during welding. When the pre-weld cleaning is not enough, the purity of the welding wire and argon is insufficient, and impurities such as nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, etc. are increased, which tends to cause the corrosion resistance of the welded portion to be lower than that of the unwelded portion, and the corrosion is first caused at the welded portion. Therefore, the less welding, the better. The pipe joint can be wrapped with a thin piece of Teflon tape (raw tape) for protection. 3·2 carbon steel and stainless steel Carbon steel heaters are only suitable for chemical or electric degreasing, zincate galvanizing and hot water bath heating. Stainless steel is also more resistant to corrosion due to the easy passivation of the surface. When the surface passivation film is destroyed by C1-, fluoride, etc., it is quickly rusted and rotted. Under the acid air corrosion of the electroplating workshop, stainless steel is used as the rectifier casing, fan and stainless steel standard, and it is also rusting very quickly. Stainless steel is divided into ferrite (such as 0Crl3), semi-ferritic (such as 1Crl3), martensite (such as 2Crl3), austenoid (such as 0Crl8Ni9, 1Crl8Ni9, 1Crl8Ni9Ti, etc.), of which 1Crl8Ni9Ti is the most widely used (commercially decorated) Stainless steel is cost-effective and contains no more Ni or Ti). Under pure reducing media conditions, some corrosion resistance is better than titanium. For example, 1Crl8Ni9T, i has a mass fraction of 50%, and the annual corrosion rate of phosphoric acid in boiling state is 0.061 mm, while the annual corrosion rate of titanium in 50% phosphoric acid at 35 ° C is 0.46 mm. If Crl8Mnl0Ni5Mo3 containing molybdenum and manganese is used, the annual corrosion rate of 50% phosphoric acid at 80 °C is only 0.003 mm; after quenching at 1050 °C, it is 0.05 mm when boiling. Therefore, in the case of chemical or electrochemical polishing of phosphoric acid or phosphoric acid-sulfuric acid, it is more preferable to use such stainless steel than titanium. 1Crl8Ni9Ti stainless steel is not resistant to corrosion in bright acid copper and aluminum sulfate anodizing solution (annual corrosion rate of 2·0mm-5·0mm at 20°C in 10%-50% sulfuric acid). High-priced Cu2+ in acid copper solution is not corrosion-resistant to stainless steel, which is different from titanium. The molybdenum-containing stainless steel has better corrosion resistance in dilute sulfuric acid solution, and the annual corrosion rate of 20% sulfuric acid at 20 ° C is less than 0.1 mm. However, Crl8Nil2Mo2Ti containing molybdenum stainless steel or Crl8Mnl0Nil5Mo containing manganese molybdenum stainless steel is also expensive to buy. Large-scale aluminum alloy sulfuric acid anodizing solutions can be ordered for processing with large coolers. 3·3 non-metallic material 3·3·1 glass The fluorine-free pure reducing medium can be a straight tube vertical electric heater with a glass tube outer casing. Ordinary glass tube is not suitable for bursting. It is necessary to use 95 heat-resistant glass or quartz glass tube. The latter price is very high. The glass heating tube is easily damaged, and the PP tube with the inner diameter of the jacket hole larger than the outer diameter of the glass tube is protected by a PP tube. Glass materials cannot be used as cooling tubes. 3·3·2 PTFE The heating and cooling of the fluorine-containing solution can only be used with polytetrafluoroethylene, and can also be used when heating and cooling the pure reducing medium. When steam heating or water cooling, a plurality of fine polytetrafluoroethylene tubes can be used as a bundle tube type heat exchanger to be used in a solution, but the space occupied is large, and the plating tank should be designed to be wider. If the electric heating tube is directly passed through the electric heating wire in the Teflon tube, the tube should be thick and the mechanical strength is sufficient, but the thermal conductivity is poor. Most of them are made of metal electric heater jacket thin Teflon tube for protection against corrosion. If the sleeve is too tight, the thermal expansion coefficient of the metal tube and the plastic tube is greatly different, and the plastic tube is easy to crack. If the gap is too large, the thermal conductivity is lowered. When the outer layer is damaged due to aging, it should be replaced in time. 4. Surface power problem of electric heater There are many types of electric heaters: vertical single-tube straight tube, shrink tube-shaped W-shaped, and bottom-heated L-shaped. When using titanium, the W-shaped tube can only be used once and cannot be repaired. Straight tube vertical and L-shaped can be repaired. There are two power indicators for electric heaters: one for the total power of each heating tube and two for surface power. The total power required for the entire bath is related to the volume of the bath, the temperature and time required for heating, and whether the tank has a thermal insulation layer. For design, refer to the relevant design manual. The surface power refers to the electric power distributed on the unit surface area of ​​the heated part of the heater, which is also called the surface load. The unit is usually expressed by W/cm2. Some people lack understanding of the surface power. To save money, always think that the power of a small heater is as high as possible. It is wrong and the service life is very short. There are several factors to consider when choosing surface power: (1) The thermal conductivity of the heater is good or bad The greater the thermal conductivity of the heater, the faster the heat transfer and the internal heating wire is not easily overheated. Common materials thermal conductivity: copper > aluminum > titanium > iron > stainless steel > glass > polytetrafluoroethylene plastic. Although copper and aluminum have good thermal conductivity, they are not resistant to corrosion and can only be used for water heating. (2) The solution conducts heat or not The thermal conductivity of the solution itself is not much different, depending on the speed of convection. When stirring with air, the convection is fast. However, it is not suitable for all solutions, and usually the solution does not open with air when it is not working (for example, when the plating solution is heated in advance in a single shift). (3) Heater arrangement When the L-shaped bottom is heated, the natural convection of the solution is better; the groove side is heated, the convection is poor, sometimes the surface liquid temperature is already high, the bottom liquid temperature is very low, and the upper and lower temperature difference is large; the upper part of the electric heater is easily overheated. (4) The electric heater is made well or not When the spiral electric heating wire is closely wound and the spacing is not uniform, the surface power of the over-tight section is too large, that is, the surface power is not uniform, and the distance between the heating wires is easy to be overheated and blown. When the thermal insulation of the filler for internal insulation of the electric heater is poor, the actual surface power is too small, and the internal heating wire is overheated and easily damaged. The surface power can usually be selected according to the following parameters: titanium material: about 3W/cm2, stainless steel 2·5W/cm2, 95 heat-resistant glass 1. 8W/cm2, quartz glass 2·2W/cm2; polytetrafluoroethylene 0· 5W/cm2. Note: The area of ​​the heated part can only be used as the calculated area. 5. Automatic temperature control 5·1 choice of thermostat Most of the automatic temperature control for industrial applications does not require high precision, since the applicable process temperature allows a certain range. Conversely, too high accuracy results in frequent temperature-controlled actuators with additional problems, allowing temperature errors of at least 1 °C - 2 °C. High-precision temperature control also increases the cost of temperature control; for electroplating, it focuses on long-term operational reliability of work and corrosion resistance under harsh corrosive atmosphere conditions. 现代温控器最好ä¸å†ç”¨æŒ‡é’ˆåŠ¨åœˆå¼ä»ªè¡¨æ˜¾ç¤ºçš„,而宜用éšæ—¶èƒ½æ˜¾ç¤ºæ¸©åº¦æ•°å€¼çš„LEDå‘光数ç 管数å—显示的。ä¸ä¸€å®šè¦ç”¨ç”µè„‘控制的å°åž‹æ¸©æŽ§å™¨,这类温控器售价较高,电æºéƒ¨åˆ†å¤šé‡‡ç”¨å®šåŽ‹è¾“出的高频开关电æº,å› æ•£çƒè¦æ±‚良好,仪表壳上有散çƒçª—å£è€Œä½œä¸åˆ°å…¨å¯†å°,故其防蚀性差,å•æœºå®‰æ”¾åœ¨å·¥è‰ºæ§½é™„è¿‘å而寿命ä¸é•¿ã€‚自动线生产时,安在è…蚀性å°çš„专用控制机柜ä¸å¯ä»¥é‡‡ç”¨ã€‚æ¤æ—¶æµ‹æ¸©æŽ¢å¤´å¼•çº¿æœ‰æ—¶å¾ˆé•¿,应对其å¯èƒ½å¸¦æ¥çš„æ¸©åº¦è¯¯å·®åŠ ä»¥ä¿®æ£ã€‚ ä¸åŒå½¢å¼çš„测温探头与相应é…套的温控器,ä¸èƒ½äº’æ¢ã€‚ å› æ¤,ä¸€èˆ¬é‡‡ç”¨å”®ä»·å‡ å元一å°çš„ã€ä½“积ç¨å¤§çš„ã€é¢æ¿åŠ 有é€æ˜Žé˜²æŠ¤ç›–çš„ã€ç”¨å¤šåœˆç”µä½å™¨è°ƒæ•´é¢„置温度的å•ç‚¹è®¾ç½®çš„LED数显温控器å³å¯ã€‚温控器上有未密å°ä¹‹å¤„åº”è´´èƒ¶å¸¦åŠ ä»¥å¯†å°ã€‚åŽæ¿æŽ¥çº¿æ¡©å¤´æˆ–æŽ¥çº¿æŽ’åœ¨æŽ¥çº¿æ— è¯¯åŽæœ€å¥½ç”¨é€æ˜Žèƒ¶çº¸ç²˜è´´åŠ 以密å°,å¦åˆ™å—æ½®å—è…åŽä¼šå‡ºçŽ°çº¿é—´æ¼ç”µå¤±çµã€æŽ¥è§¦ä¸è‰¯ç‰æ•…障。 5·2 测温探头的选择 5·2·1 测温元件 对一般电镀溶液,工作液温都低于100℃或在100℃左å³,宜选用Ptl00铂电阻的。它在低温下应用的分辨力较高ã€è¯¯å·®è¾ƒå°ã€‚铂电阻具有æ£æ¸©åº¦ç³»æ•°:éšæ¸©åº¦ä¸Šå‡,其阻值å˜å¤§;温控仪将其总阻值(包括引线电阻)转æ¢ä¸ºå¯¹åº”温度值示出。其阻值与温度之间并éžå‘ˆçº¿æ€§å…³ç³»ã€‚å› è€Œé“‚ç”µé˜»ç”¨äºŽç²¾å¯†æµ‹æ¸©æ—¶,温控器内都有一套å¤æ‚的温度线性补å¿ç”µè·¯ã€‚工业测控时则未设线性补å¿ã€‚æ£æ¸©ç³»æ•°å¯ä»¥ä»Žæ•°æ˜¾å™¨ä¸Šåˆ¤å®šå…¶æŸå与å¦;当输入至温控器的线路(包括铂电阻本身或接线)å‘生çŸè·¯æ—¶,在任何温度下å‡æ˜¾ç¤ºè´Ÿæ¸©åº¦å€¼(输入电阻接近零),当铂电阻烧æ–或探头接线æ–线时,æ¸©æŽ§å™¨å› è¾“å…¥ç”µé˜»å¾ˆå¤§ç”šè‡³æ— ç©·å¤§,则显示æ£800℃多。由æ¤å¯ä»¥è¯Šæ–探头是å¦å› 进液而çŸè·¯æˆ–æ–线而开路的æŸå情况。尽管铂电阻ç†è®ºä¸Šå¯ç”¨åˆ°500℃,但实际上市售å多元一支的铂电阻探头组件都是劣质产å“。å¯ç”¨,但温度高åŽåˆ™å¤–套瓷管会æ–裂,所以ä¸èƒ½è¶…过120℃使用(æ£å®—铂电阻è¦60余元一支)。故用于钢é“件高温碱性å‘è“åŠçƒæµ¸é•€é“…锡åˆé‡‘的测控温时,宜采用çƒç”µå¶å¼æŽ¢å¤´ã€‚çƒç”µå¶å¯æµ‹è¾ƒé«˜æ¸©åº¦,但测低温时误差较大。 铜电阻探头的çƒæƒ¯æ€§è¾ƒå¤§,一般很少用。åŠå¯¼ä½“测温探头çµæ•åº¦é«˜ã€å“应速度快,但互æ¢æ€§å·®,温控器线路å¤æ‚。笔者自己开å‘è¿‡å‡ æ¬¾,但市售å“æžå°‘,也åªé€‚于低温用。 5·2·2 探头的防è…蚀问题 测温探头用外壳æ料应è€ç›¸åº”介质的è…蚀。 一般情况下宜用钛质的,碱性å‘è“ç‰é«˜æ¸©çƒç”µå¶å¯ç”¨ä¸é”ˆé’¢æ质。但市售探头外壳多数为紫铜管å°å¤´åŽé•€è–„层装饰铬的,直接用于电镀液会被很快è…蚀穿å”进液而æŸå。è¦æ”¹æˆé’›æˆ–ä¸é”ˆé’¢çš„,则è¦æ‰¾è®¾å¤‡åˆ¶é€ 厂定åšåŠ 工。 è‹¥æ— æ¡ä»¶æ”¹æ¢æ质时,也å¯ä½œç®€æ˜“处ç†(应è´è¾ƒé•¿çš„探头),用于一般电镀低温液: (1)用“生料带â€(èšå››æ°Ÿä¹™çƒ¯è–„带)å¯¹æŽ¢å¤´å¤–è¡¨å¯†å®žç¼ ç»•3-4层(注æ„å¤´éƒ¨åº”ç¼ å®žæ— æ¼å‡ºå¤„); (2)用内径略大于探头管外径的çƒç¼©ç®¡è¿›è¡Œçƒç¼©ä¸€å±‚塑料管,端头乘çƒç”¨é’³å夹紧çƒç¼©ç®¡ä»¥å¯†å°åº•éƒ¨ã€‚ 使用时ä¸å¯ç¢°å外ä¿æŠ¤å±‚。也å¯å¤–套钻å”PPç®¡åŠ ä»¥ä¿æŠ¤(PPæ料在强氧化性的镀铬液ä¸ä¼šå—è…蚀)。 安装å‰å¯¹å¼•çº¿å¼•å‡ºéƒ¨ä½å…ˆç”¨åŠ çƒçŸ³èœ¡æˆ–鱼烛滴入进行密å°å¤„ç†,以å…è…蚀性气体或蒸汽浸入冷å‡é€ æˆçƒæ•å…ƒä»¶å—æ½®ã€è…蚀。也易于拆æ¢çƒæ•å…ƒä»¶ã€‚安装在ä¸æ˜“å—碰的è·åŠ çƒå™¨ä¸€å®šè·ç¦»çš„槽内侧å£ä¸Šã€‚务必安装牢固(大生产ä¸å¸¸å‡ºçŽ°å·¥äººä¸å°å¿ƒå°†æŽ¢å¤´è½å…¥é•€æ¶²è€Œè¿›æ¶²å¤±çµã€æŸå的问题)。 5·3 温度误差问题 溶液实际温度与温控器数å—æ˜¾ç¤ºå€¼ä¹‹é—´çš„å·®å¼‚ä¼šé€ æˆæµ‹æŽ§è¯¯å·®ã€‚ 5·3·1 误差æ¥æº (1)温控器本身质é‡é—®é¢˜ 工业用温控器现售价都低,ç²—åˆ¶æ»¥é€ å“ä¸å°‘。有的线路元器件ä¸è‰¯ã€çº¿è·¯è¿‡äºŽç®€å•ã€ç¨³åŽ‹ç”µæºç¨³åŽ‹ç²¾åº¦å·®ã€å‡ºåŽ‚å‰è°ƒæ ¡ä¸è®¤çœŸç‰,本身误差就大。è´ä¹°æ—¶åº”当场接上é…套探头,于çƒæ°´ä¸ç”¨æ ‡å‡†æ¸©åº¦è®¡æµ‹å®š,误差过大的则ä¸èƒ½ç”¨ã€‚ (2)测温探头互æ¢æ€§å·® 有å¯èƒ½å‡ºåŽ‚æ ¡éªŒæ—¶ç”¨çš„è‰¯å“探头(电阻å¼ç”¨æ ‡å‡†é˜»å€¼ç”µé˜»ä»£æ›¿æŽ¢å¤´)调试,而è´ä¹°çš„劣质探头在相应温度下阻值ä¸æ£ç¡®(电阻å¼),æ¢ä¸€ä¸ªæŽ¢å¤´è¯»æ•°åˆä¸ä¸€æ ·ã€‚ (3)æŽ¢å¤´å¼•çº¿ç”µé˜»å½±å“ é“‚ç”µé˜»ä¹‹ç±»å”®å“探头引出线çŸ,å®žé™…ä½¿ç”¨æ—¶åŠ é•¿æŽ¢å¤´çº¿,会增大串è”总阻值,线径越细,é™„åŠ ç”µé˜»å¤§,读数越å高。çƒç”µå¶æŽ¢å¤´ç”¨çº¿èµ·è¡¥å¿ä½œç”¨,ä»»æ„åŠ é•¿æˆ–å‡çŸéƒ½å¼•å…¥è¯¯å·®ã€‚æœ‰æ—¶åŠ é•¿å¼•çº¿æ—¶æŽ¥å¤´å¤„æŽ¥è§¦ä¸è‰¯æˆ–ç»ç¼˜ä¸è‰¯é€ æˆæ¼ç”µä¹ŸåŠ 大或å‡å°æ¸©æŽ§å™¨è¾“入电阻,应å分注æ„。 5·3·2 误差消除法 (1)é‡æ–°è°ƒæ ¡æ¸©æŽ§ä»ªã€‚温控仪内部有å¯è°ƒæ ¡æ˜¾ç¤ºæ•°å€¼çš„微调电阻。对电å电器熟悉的人å¯æ‹†å¼€æ¸©æŽ§ä»ªé‡æ–°è°ƒæ ¡ã€‚ä¸æ‡‚的人切ä¸å¯ä¹±è°ƒã€‚ (2)确认相对误差,设置控制温度。准备一支准确的水银或煤油温度计,在欲控温度值(例如对亮é•æ¶²è®¾ä¸º55℃)时看温控器数值显示值(例如为58℃),则将温控器预置温度设定为该值(58℃)。 5·4 功率放大 温控器内的å°ç»§ç”µå™¨å…许电æµå¾ˆå°,ä¸èƒ½ç›´æŽ¥è¿žæŽ¥è´Ÿè½½,而è¦ç”¨äº¤æµæŽ¥è§¦å™¨æ¥æ”¾å¤§å…许承载功率:温控器å°ç»§ç”µå™¨æŽ§åˆ¶äº¤æµæŽ¥è§¦å™¨çº¿åœˆç”µæµçš„通æ–,交æµæŽ¥è§¦å™¨ä¸»è§¦å¤´ä¸²åœ¨è´Ÿè½½å›žè·¯ä¸ã€‚åŒä¸€å°æ¸©æŽ§å™¨æŒ‰ç…§ä½¿ç”¨è¯´æ˜Žä¹¦æŽ¥çº¿è¦æ±‚,æ—¢å¯æŽ¥æˆåŠ çƒæ’温控制也å¯æŽ¥æˆåˆ¶å†·æ’æ¸©æŽ§åˆ¶ã€‚åŠ çƒæ’温控制时,液温下é™åˆ°é¢„置温度时,交æµæŽ¥è§¦å™¨å¸åˆ,ä¸»è§¦å¤´æŽ¥é€šåŠ çƒæº(ç”µåŠ çƒæ—¶çš„ç”µåŠ çƒå™¨,è’¸æ±½åŠ çƒæ—¶çš„供汽电ç£é˜€)。制冷控制时,温度上å‡åˆ°é¢„置温度时,交æµæŽ¥è§¦å™¨å¸åˆ,主触头接通制冷机å¯åŠ¨æˆ–接通冷å´ä¾›æ°´çš„冷水电ç£é˜€ã€‚å离预置温度1℃-2℃则作相å动作。 当槽液体积大,ç”¨å¤šç»„ç”µåŠ çƒå™¨åŠ çƒæ—¶,ä¸ä¸€å®šéœ€è¦åŒæ—¶é€šæ–æ‰€æœ‰åŠ çƒå™¨ç”µæº,å¦åˆ™äº¤æµæŽ¥è§¦å™¨æ‰€éœ€åŠŸçŽ‡å¤ªå¤§,动作频ç¹ã€‚å¯æ®è¯•éªŒç»“æžœæŽ§åˆ¶éƒ¨åˆ†ç”µåŠ çƒå™¨,其余则一直工作ä¿æ¸©ã€‚ 6.æº¶æ¶²çš„å†·å´ ä¸€äº›å·¥è‰ºä¸å…许液温较高,如镀锌(特别是滚镀锌)ã€ç¡«é…¸ç›å…‰äº®é…¸æ€§é•€é“œä¸Žé•€é”¡ã€é“件硫酸阳æžæ°§åŒ–(特别是硬质氧化)ç‰ã€‚当超过工艺液温上é™å€¼æ—¶,应对镀液é™æ¸©ã€‚ 6·1 简易é™æ¸©æ³• 当镀液温å‡é€Ÿåº¦ä¸å¿«ã€æ¸©å‡å‘çƒé‡ä¸å¤§æ—¶,å¯ç”¨ç›¸åº”工艺的è€è…蚀钛ã€èšå››æ°Ÿä¹™çƒ¯è›‡å½¢ç®¡æˆ–盘管置于镀液ä¸é€šå…¥åœ°ä¸‹æ°´å†·å´é™æ¸©;采用夹套槽时,则于夹套层ä¸é€šå…¥å†·æ°´é™æ¸©,出水循环冷å´åŽå†åˆ©ç”¨æˆ–用作清洗用水。一般情况下ä¸ä½œè‡ªåŠ¨æ¸©æŽ§,控温仪供测温用,手动控制冷å´æ°´è¿›æ°´é‡å³å¯ã€‚ 6·2 åˆ¶å†·æœºå†·å´ å½“é•€æ¶²å‘çƒé‡å¤§ä¸”温å‡å¿«,水冷ä¸è¶³ä»¥é™æ¸©æ—¶,则åªå¥½é‡‡ç”¨åˆ¶å†·æœºé™æ¸©ã€‚如高负è·ä¸‹çš„光亮酸铜ã€é…¸é”¡æ¶²,特别是å¤å¤©é“件硫酸阳æžæ°§åŒ–液与必须-5℃至+5℃的é“件硫酸硬质阳æžæ°§åŒ–。 ä¸ä¸»å¼ 用冷å´ç®¡ä¸ç›´æŽ¥é€šå…¥æ°Ÿé‡Œæ˜‚çš„è€å¼åˆ¶å†·æ–¹æ³•ã€‚å› æ˜“æ¸—æ¼å‡ºçš„æ°Ÿé‡Œæ˜‚ä¼šç ´å高空è‡æ°§å±‚。电冰箱早就ç¦ç”¨æ°Ÿé‡Œæ˜‚制冷方法。宜用冷水机循环通入ç»åˆ¶å†·æœºå†·å´åŽçš„低温水进行é™æ¸©ã€‚需è¦çš„制冷é‡åº”先通过计算确定,å¯å‚è§æœ‰å…³è®¾è®¡æ‰‹å†Œã€‚ 6·3 在硫酸阳æžæ°§åŒ–ä¸é’›è´¨å†·å´ç®¡çš„应用问题 由于é“件硫酸阳æžæ°§åŒ–应用较多,ä¸”å‡ ä¹Žéƒ½è¦å†·å´,常用钛管作冷å´ç®¡ã€‚å…¶é˜²èš€æ€§é—®é¢˜å¿…é¡»åŠ ä»¥å¼ºè°ƒã€‚ 6·3·1 防æ¢é’›ç®¡è…蚀 é’›ä¸è€çº¯è¿˜åŽŸæ€§ä»‹è´¨çš„è…蚀。稀硫酸是还原性介质,硫酸阳æžæ°§åŒ–液ä¸é“离ååªæœ‰ä¸‰ä»·æ€,è€Œæ— ä½Žä»·å’Œé«˜ä»·æ€,对钛的è…蚀ä¸å…·ç¼“蚀能力。表1进一æ¥åˆ—出了工业纯钛在ä¸åŒè´¨é‡åˆ†æ•°ã€ä¸åŒæ¶²æ¸©ä¸‹çš„å¹´è…蚀率。å¯è§æµ“度越高ã€æ¶²æ¸©è¶Šé«˜,è…蚀越快。ä¸å‘ˆçº¿æ€§å…³ç³»,60%æ—¶å低些。 硫酸阳æžæ°§åŒ–液ä¸ç¡«é…¸çš„è´¨é‡åˆ†æ•°åœ¨10%-38%之间,钛的è…蚀很快:先呈ç°è‰²,然åŽç‚¹èš€,å†å‡è–„ç©¿å”æŸå。 6·3·2 应对措施 (1)é…液时ä¸èƒ½æ”¾å…¥é’›å†·å´ç®¡ã€‚é…制硫酸阳æžæ°§åŒ–液时,在ä¸æ–æ…æ‹Œä¸‹æ…¢æ…¢å°†æµ“ç¡«é…¸åŠ å…¥æ°´ä¸ã€‚æ°´åˆå应是强烈放çƒå应,液温很快å‡é«˜ã€‚若先将冷å´é’›ç®¡æ”¾å…¥æ§½ä¸,则在高液温下钛管立å³è¿…速被è…蚀。åªèƒ½å°†æ§½æ¶²è‡ªç„¶å†·å´è‡³å®¤æ¸©åŽæ‰èƒ½æ”¾å…¥å†·å´ç”¨é’›ç®¡ã€‚ (2)人为电解氧化。é…液冷å´åŽå°†å†·å´é’›ç®¡æ”¾å…¥,接上直æµç”µæºã€é˜´æžä¸Šæ”¾å¥½é“…æ¿,将钛管直接接æˆé˜³æž,以约3A/dm2的电æµå¯†åº¦é˜³æžæ°§åŒ–æ•°å°æ—¶,直至钛管表é¢å…¨éƒ¨å‘ˆæ£•è‰²ã€‚ (3)一直作阳æžä¿æŠ¤ã€‚钛在硫酸ä¸çš„阳æžè‡´é’电æµå¯†åº¦è¾ƒå¤§(40%ç¡«é…¸ä¸çº¦0·3mA/cm2)。但一旦人为氧化é’化åŽ,ç»´æŒé’化的维é’电æµå¯†åº¦å´å¾ˆå°,(40%ç¡«é…¸ä¸ä¸º0·5μA/cm2-1·0μA/cm2)ã€‚å› æ¤,平时工作与未工作时å¯ç”¨ä¸€å°æ•´æµå™¨,阳æžæŽ¥é’›å†·å´ç®¡ã€é˜´æžæŽ¥æ°§åŒ–用阴æžé“…æ¿(冷å´ç®¡ä¸Žé“…æ¿åº”ç»ç¼˜è€Œä¸èƒ½ç›¸ç¢°),一直通电作阳æžä¿æŠ¤(ä¸ç”Ÿäº§æ—¶ä¹Ÿä¸èƒ½æ–电)。电æµå¯†åº¦å¤§äºŽç»´é’电æµå¯†åº¦å³å¯ã€‚ 测试表明,对40%ç¡«é…¸,在60℃时,é’›çš„å¤–åŠ ç”µä½(æ’电ä½æ³•)è¾¾+2·1Væ—¶,其年è…蚀率仅0·005mm,é™ä½Žäº†11000å€ã€‚ 生产实践è¯æ˜Ž,采用上述3项对ç–åŽ,é“硫酸阳æžæ°§åŒ–液ä¸çš„冷å´é’›ç®¡å¯é•¿æœŸä¸è…ã€‚æœªåŠ é˜³æžä¿æŠ¤çš„,则很快被è…蚀而å‘ç°ã€ç©¿å”。 Concerned about surprises æ ‡ç¾:溶液 电镀设备 过滤机 ç£åŠ›æ³µ é“件 上一篇 : 家装å°è´´å£«ï¼šå‡ æ‹›æžå®šé”具选择 下一篇 : é•ç¢³åŒ–钨纳米å¤åˆé•€å±‚的制备与性能 Glass Smoking Pipe,Green Hookah Shisha,Glass Pipes Hookah,Hookah Shisha Ss.Art Hookah Co., Ltd , http://www.zjhookah.com