I System description:
Heat Shrinkable Tape is designed to protect the weld joint of buried or exposed steel pipelines and insulated pipeline. This sleeves are manufactured from high quality cross linked polyethylene material. Hot melt adhesive provides excellent adhesion with the surface of steel pipeline, PE coating. Meanwhile it forms a continuous and firm anti-corrosive system with the surface of the pipeline.
The Polyethylene Heat shrinkable Tape needs no primer nor patch closure and reduces application time and labour costs.
â…¡ Structure
The specification of the tape consists of three layers,
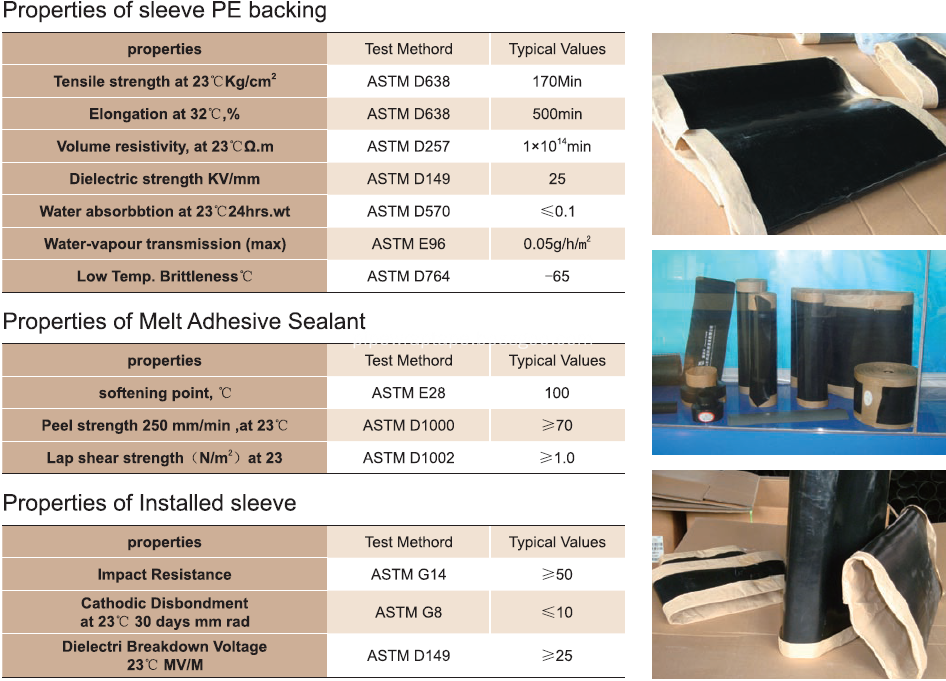
Adhesive: butyl rubber based hot melt adhesive
Film backing: Radiation crosslinked polyethylene
Interleaf:Antiadhesive Film Treated with Silicone
â…¢ Features
After heating, formed corrosion protection seal
Strong backing provides outstanding waterproofing effect
High chemical resistance. resists impact, abrasion and ultraviolet light.
Excellent resistance against cathodic disbondment, dielectric breakdown.
Simple Application
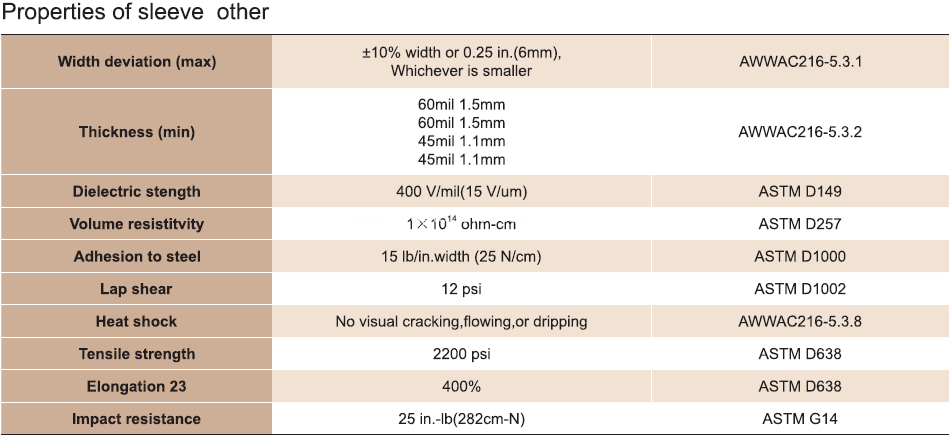
â…£ Physical Properties
· Product Data Sheet Total Thickness:40mil, 50 mil,60 mil ,65 mils.
· Width:50,100,150,300,400,500,800 mm
· Length: 10 m
· Tensile Strength:35 N/cm
· Elongation:400%
· Adhesion Strength to pipe:30 N/cm
· Application temperature: -10 -60 ℃
· Temperature resistance:-50 ℃ - 80℃
· Shelf Life: 12 months
â…¤ Application
No Special skills, equipments, patch closure nor primer are needed. Its superior flexibility provides easy and reliable application for irregular configurations of fittings, bends and elbows and small diameter of straight pipes
Wrap spirally the tape over foreign matters-free and preheated surface, beginning at least 25~50mm (1~2 ) onto pipe coating. Wrap the tape with enough tension to obtain conformability and with minimum 50% of overlapping, while removing the release liner. Warm the end part of the tape and press down firmly. Using a torch, start at the edge of the tape and heat circumferentially around the coated pipe.
Finish off by heating over the entire tape vertically to ensure a uniform adhesion and by using a roller or gloved hands to remove wrinkle and air.
VI. Technical Datas
Hot Shrink Adhesive Tape, Heat Shrinkable Electrical Tape, Heat Shrinkable Wrap Tape, Shrinking Tape, Heat Applied Tape Coating System Jining Xunda Pipe Coating Materials Co.,Ltd , http://www.pipe-wrap.com

7 materials help to improve the wear resistance of plastic products
There are several obvious ways to damage the surface of plastic products , including scratches of sharp objects; wear caused by abrasive friction; surface damage that changes surface properties or gloss; or "writing effect" caused by slight scratching of passivated objects. The reason for these phenomena is that the material yields under the action of the pressing force and the sliding force or the lateral (side) direction force, causing ductile/brittle damage to cause scratches. In scratches, uneven surfaces create uneven light scattering and "scratch". The solution to improve the scratch performance is to minimize the roughness of the underside of the polymer and reduce the scratched shoulders, resulting in as little light scattering as possible and as little scratch visibility as possible, thus achieving a higher wear resistance. performance.
Some plastics themselves have good wear resistance, and after adding various anti-wear additives, they can further improve their wear resistance. Plastic additives made of additives such as polytetrafluoroethylene, molybdenum disulfide, graphite, silicin oil, glass fiber, carbon fiber and aramid fiber have self-lubricating properties and can reduce the pressure of the mating parts. Improve the wear resistance of the material. Here are the seven materials that can improve the wear resistance of materials with the Jiuzhi Plastics Network:
1. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, Teflon)
PTFE is the lowest friction coefficient of any additive. The PTFE molecules that are ground during the rubbing process form a lubricious film on the surface of the part. PTFE has good lubricity and wear resistance under friction and shear. PTFE is the best additive in high load. These high load applications include hydraulic piston ring seals and thrust washers. The most suitable PTFE content is 15% PTFE for amorphous and 20% PTFE for crystalline plastic.
Molybdenum disulfide
Another common name for molybdenum disulfide is "Moly", which is mainly used as an additive for nylon plastics. Molybdenum disulfide acts as a crystallization agent to increase the crystallinity of the nylon to give the nylon material a harder and more abrasive surface. Molybdenum disulfide has a high affinity for metals. Once adsorbed on the metal surface, the molybdenum disulfide molecules fill the pores of the metal surface visible to the microscope and make the metal surface smoother. This makes molybdenum disulfide an ideal wear-resistant additive for applications where nylon and metal rub against each other.
Third, graphite
The chemical structure of graphite is a unique lattice structure. This unique chemical structure allows graphite molecules to slide easily across each other with little friction. This wear resistance is especially important in watery environments. This property makes graphite an ideal wear-resistant additive for many applications in water applications such as water jackets, impellers and Value seals.
Fourth, polysiloxane
A silicone fluid is a wear-resistant additive that migrates. When added to a thermoplastic, the additive slowly migrates to the surface of the part and forms a continuous film. Polysiloxanes have a wide range of viscosities and viscosities are measured in centistokes. The viscosity of the polysiloxane is too low, and it becomes fluid-like and rapidly migrates to the surface of the part to provide wear resistance. If the viscosity of the polysiloxane is too low, it is more volatile and will quickly disappear from the part.
Fifth, fiberglass
Glass fiber is a hard and highly scratch-resistant fiber, and it is often mistaken to believe that the addition of glass fiber to plastic destroys the wear resistance of the plastic. Glass fiber provides a strong mechanical bond between the polymers, so glass fiber can increase the integrity of the thermoplastic structure and improve wear resistance. The reinforcement provided by the glass fiber can increase the anti-potential, thermal conductivity and thermal deformation of the plastic, thereby significantly improving the load resistance and abrasion resistance of the plastic.
Sixth, carbon fiber
In the case of glass fiber, carbon iron can greatly improve the structural integrity, wear resistance and resistance to load and abrasion speed. Unlike glass fiber, carbon fiber is a softer and less scratch-resistant fiber. Carbon fiber does not scratch the frictional surface of the iron or steel with which it rubs. Adding more than 10% of the carbon fiber to the thermoplastic has the function of eliminating static electricity, and thus can overcome the static problem caused by the problem.
Seven, aramid fiber
Aramid fibers are also one of the wear resistant additives. Unlike fiberglass and carbon fiber, it is the softest and most scratch-free fiber. This property is a major advantage of aramid fibers in wear resistant applications, particularly in the case of mating parts that are scratch resistant to the fibers.